ISD Publications
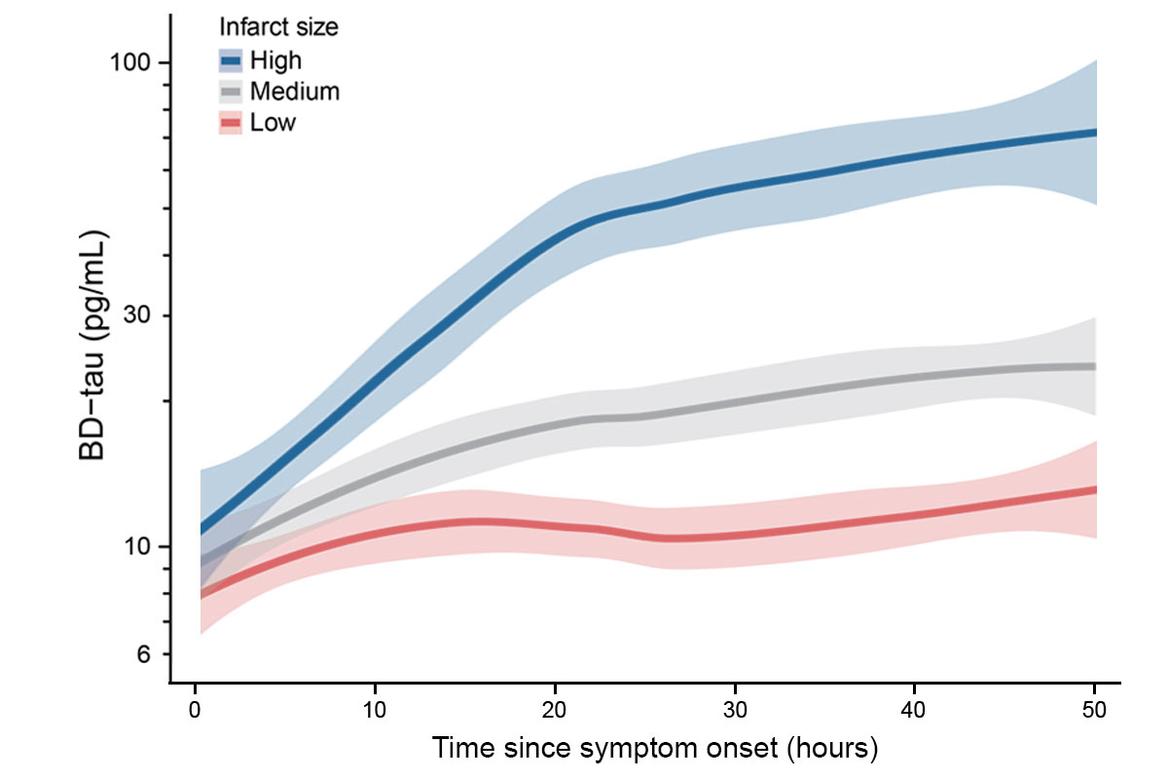
New blood test enables brain injury monitoring after stroke
January 2026 – Stroke is a medical emergency with rapidly evolving brain injury. But unlike other organs, the brain lacks a blood test to monitor acute injury. ISD researchers and international partners report that a new blood biomarker, brain-derived tau (BD-tau), can track brain injury after ischemic stroke, predict outcomes years later and reflect treatment effects. Now published in Science Translational Medicine!
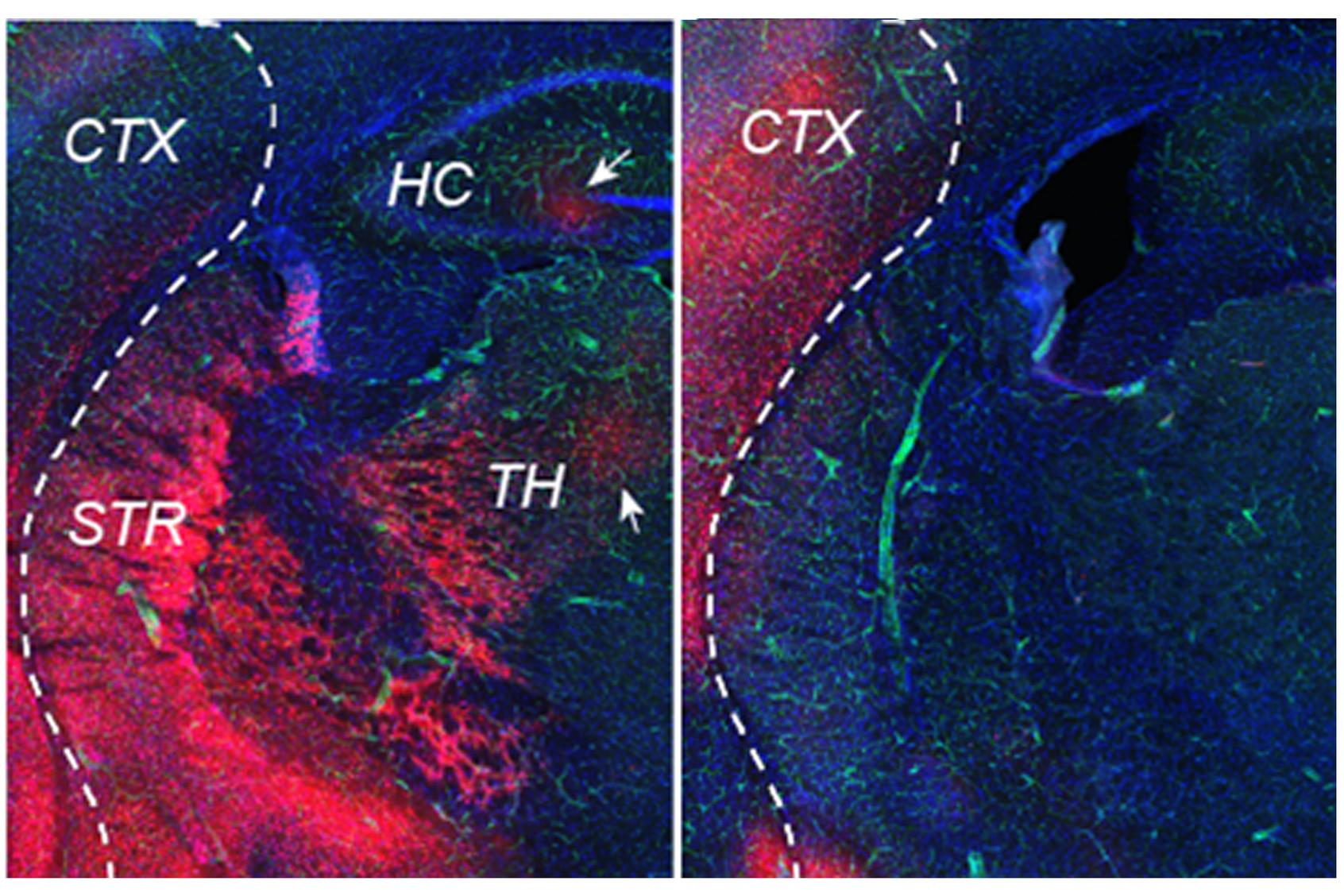
FOXF2 Protects Brain Vessels by Sustaining Tie2 Signaling
January 2026 – Small vessel disease (SVD) is a major cause of stroke, yet its molecular drivers remain elusive. ISD researchers now show that the stroke-risk gene FOXF2 is essential for maintaining healthy brain vessels by sustaining Tie2 signaling in endothelial cells. Loss of FOXF2 disrupted endothelial function, impaired blood–brain barrier integrity, and worsened outcomes after experimental stroke. Activating Tie2 with AKB-9778 rescued these deficits. The findings identify FOXF2–Tie2 signaling as a critical pathway in SVD and highlight a promising therapeutic target.
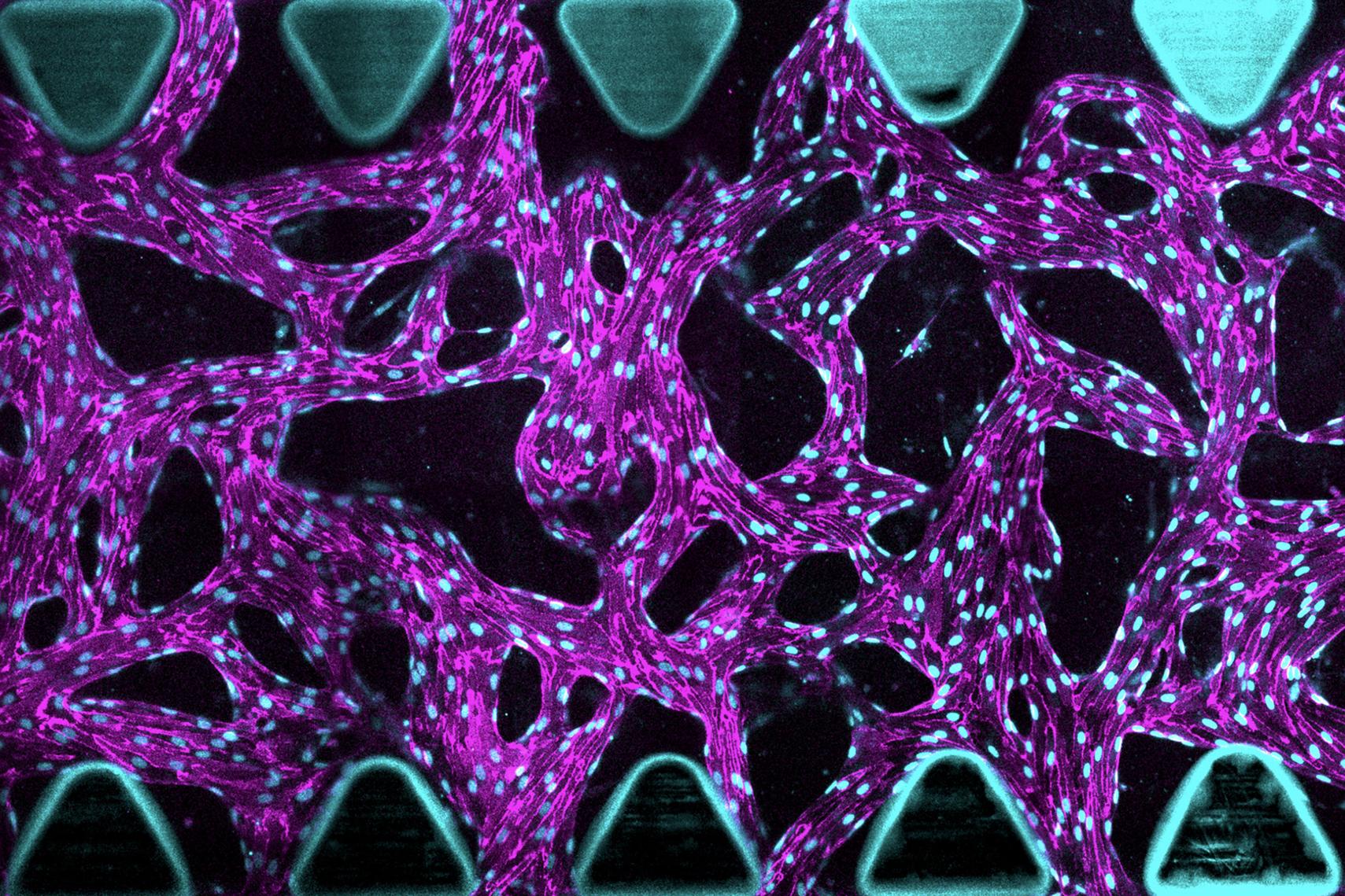
A Human 3D Model of the BBB Sheds Light on Neurovascular Diseases
January 2026 – Maintaining a functional blood–brain barrier (BBB) is crucial for brain function, but human models are needed to better understand human disease. ISD researchers developed a human BBB model from stem cells that recreates key features of brain vasculature and allows investigating disease mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. When they inactivated the stroke-risk gene FOXF2 in the BBB, the barrier became dysfunctional, which they could alleviate using an LNP-based treatment.
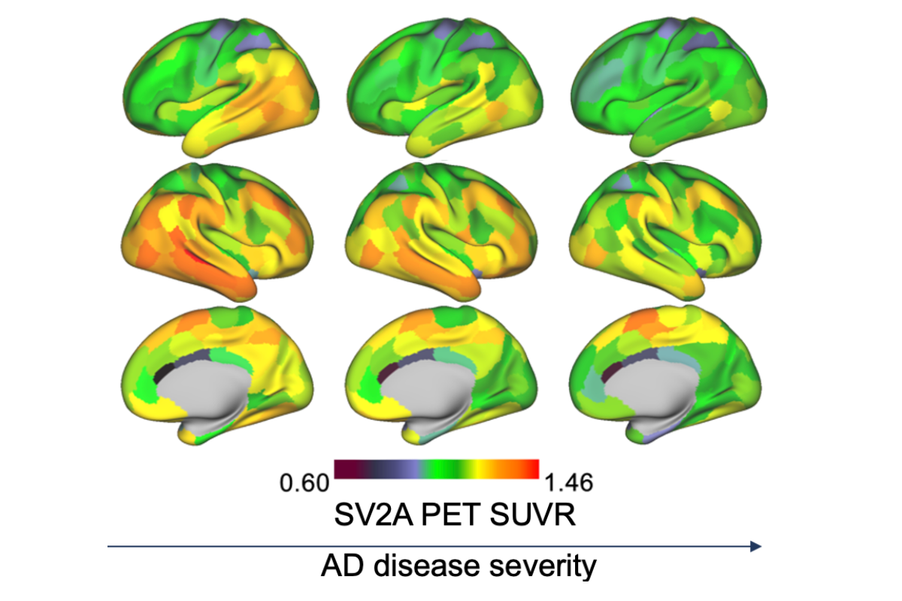
Synaptic density associated with tau pathology in AD
November 2025 – Synapses are not only essential for information transfer but also potential gateways for the spread of pathogenic processes in the brain. A study by ISD investigators found brain regions with high synaptic density to be particularly vulnerable to accumulating pathological tau in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Moreover, tau accumulation was associated with downstream synaptic loss in connected regions, suggesting that synapses play a central role in tau-related neurodegeneration.
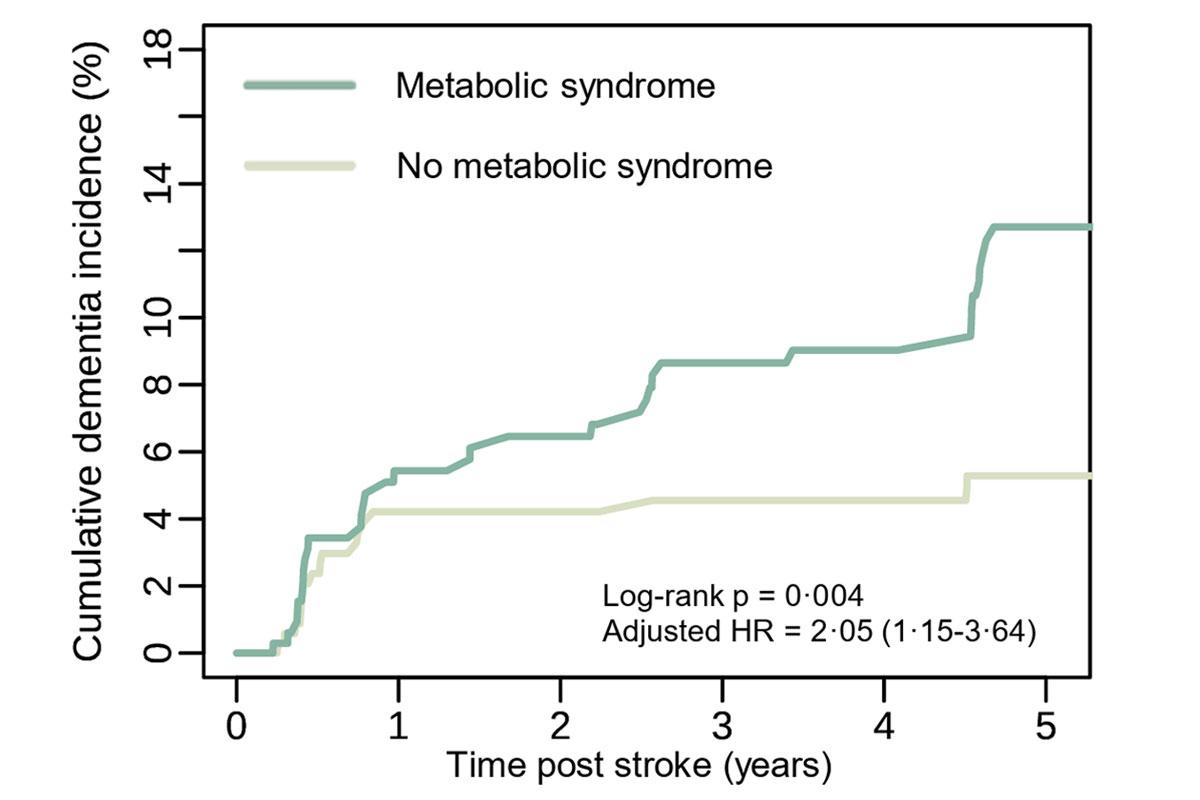
Key risk factors for post-stroke dementia uncovered
September 2025 – Front line results from the DZNE-funded multicenter DEMDAS study identify metabolic syndrome and reduced HDL cholesterol as novel, modifiable risk factors for post-stroke dementia, and reveal distinct profiles for early- and delayed-onset cases, highlighting new opportunities for targeted prevention.
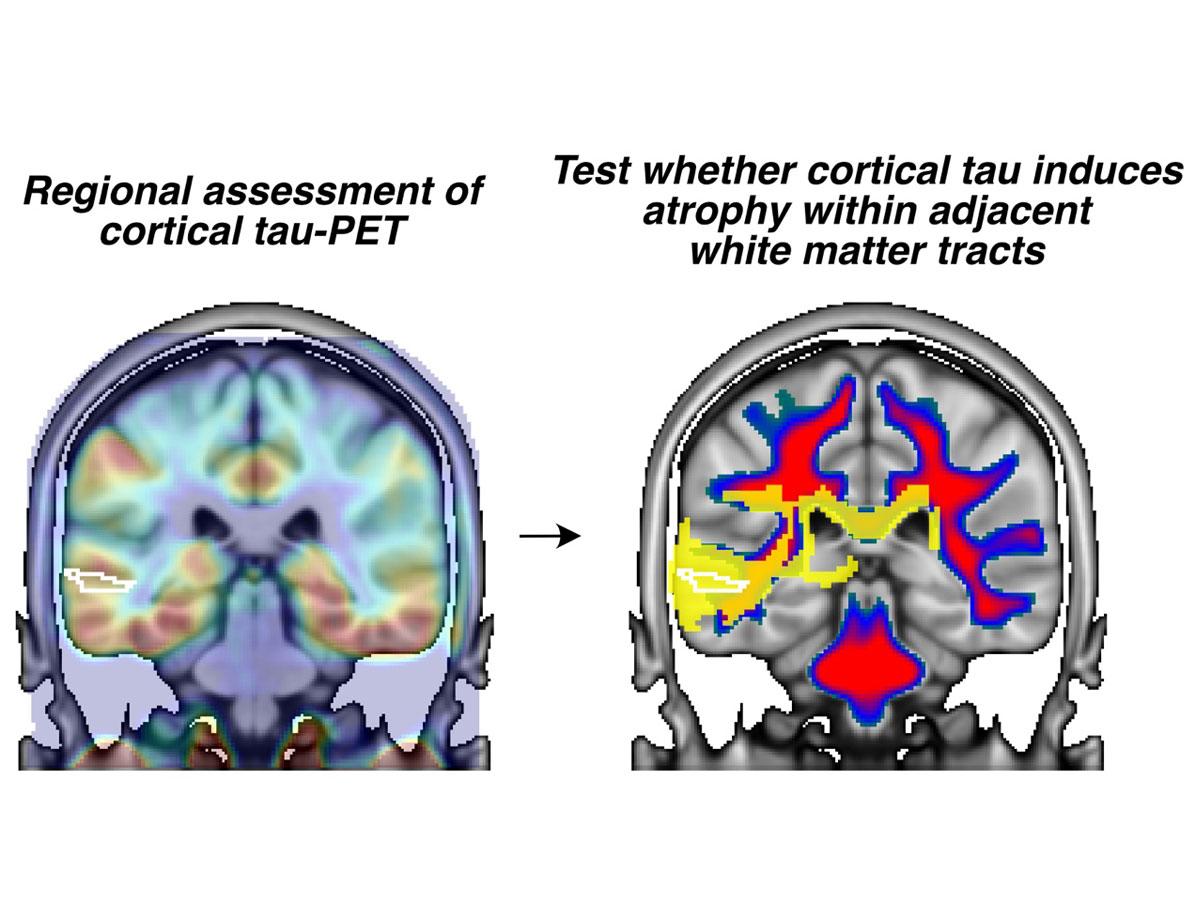
Tau deposits in Alzheimer’s linked to degeneration of white matter networks
September 2025 – A new study published in Brain, led by Nicolai Franzmeier at the ISD, shows that cortical tau deposits in Alzheimer’s disease trigger degeneration of directly connected white matter tracts. These findings demonstrate how tau pathology disrupts structural brain networks, providing key insights into Alzheimer’s progression.
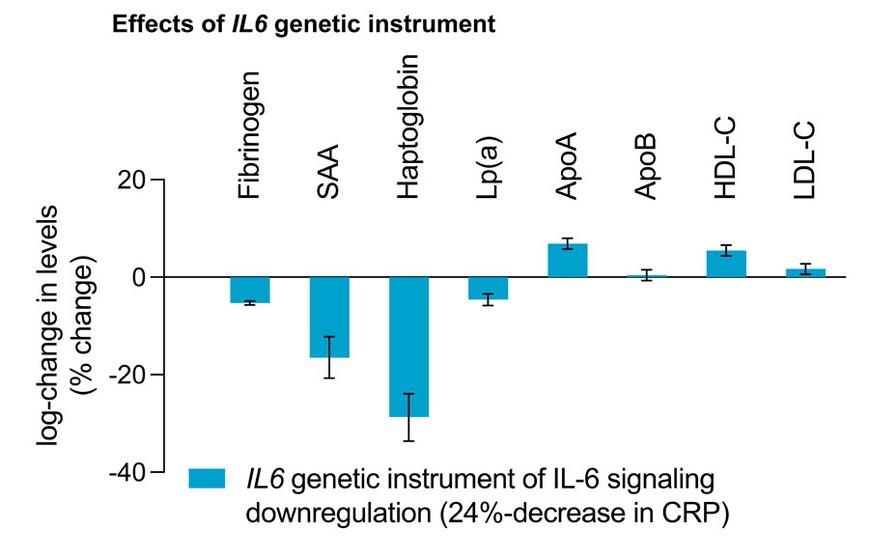
IL6 genetic perturbation mimicking IL-6 inhibition is associated with lower cardiometabolic risk
September 2025 – The team of Marios Georgakis used an IL6 genetic instrument to mimic IL-6 inhibition in over 500,000 individuals, showing reduced risks of coronary and peripheral artery disease and ischemic stroke without infection concerns— lowering pneumonia hospitalizations—supporting IL-6 inhibitors under development in ongoing cardiovascular trials.
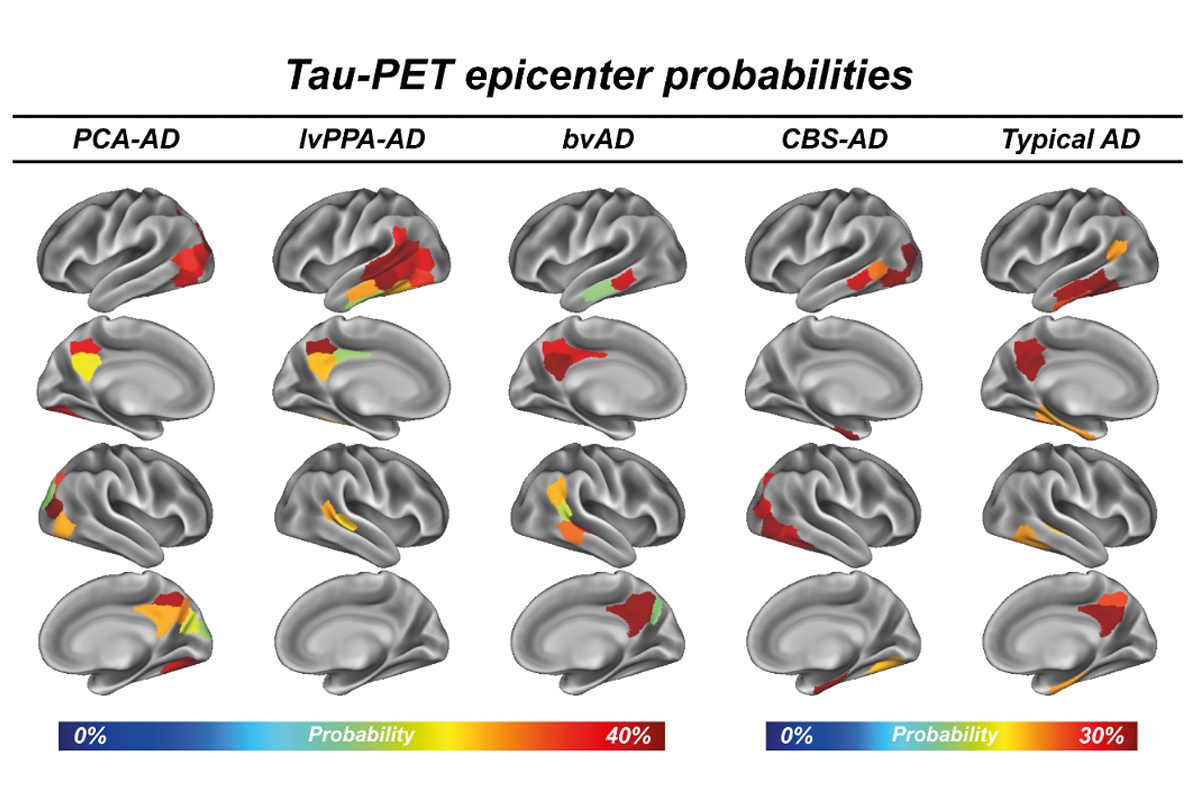
Connectivity as a universal predictor of tau progression in atypical Alzheimer’s disease
August 2025 – A multi-center study led by Nicolai Franzmeier (ISD) and Rik Ossenkoppele (Amsterdam UMC) compiled the to date largest biomarker and post-mortem dataset on atypical Alzheimer’s disease, showing distinct tau onset sites and network-based spread, supporting trans-neuronal tau propagation and informing personalized medicine and trial endpoints.

Microstrokes impair spatial memory and place cell stability
April 2025 – Using chronic 2-photon imaging in-vivo, Anna-Sophia Wahl and her team tracked the fate of individual neurons involved in spatial memory before and after multiple, distributed microstrokes. Network stability predicted cognitive outcomes, highlighting targets for preventing post-stroke cognitive decline.

Alpha-synuclein co-pathology promotes tau accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease
March 2025 – In a collaborative study, ISD researchers found that Alpha-synuclein co-pathology is more common in advanced AD and accelerates tau aggregation and cognitive decline. This underscores the need to consider αSyn in AD research and treatment strategies, particularly in amyloid-driven tau pathophysiology.

An atypical chemokine that links atherosclerosis and metabolic disease
March 2025 – Fatty liver disease exacerbates atherosclerosis, but the mechanisms are incompletely understood. A new collaborative study led by ISD investigators identifies D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT/MIF-2) as an atypical chemokine that promotes both atherosclerosis and hepatic lipid accumulation. The researchers also define the underlying receptor mechanism.

The HDAC9 risk locus controls inflammasome activation in atherosclerosis
Januar 2025 – Common genetic variants in a cis-regulatory element at HDAC9 are associated with atherosclerotic phenotypes including stroke and myocardial infarction. ISD investigators now defined a mechanism whereby HDAC9 regulates activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and developed a targeted anti-inflammatory approach for treating atherosclerosis.
Aβ promotes tau spreading by eliciting neuronal hyperconnectivity
Januar 2025 – A study led by ISD researchers suggests a key mechanistic link between Aβ and tau accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease, showing that Aβ induces neuronal hyperconnectivity, thereby promoting the spread of tau pathology across interconnected brain regions.
Novel strategy for biomarker-based amyloid diagnostics in clinical settings
November 2024 – A new collaborative study coordinated by LMU/SyNergy investigators and the University of Vienna proposes a novel clinical workflow for the reliable biomarker-based identification of amyloid pathology in memory clinic patients, in preparation of disease-modifying treatments against Alzheimer’s disease …

DNA-sensing inflammasomes cause recurrent atherosclerotic stroke
August 2024 – Using a novel experimental model, ISD researchers showed that stroke activates the AIM2 inflammasome in atherosclerotic plaques via increased circulating cell-free DNA, causing inflammation, plaque destabilization, and recurrent stroke. Neutrophil NETosis was identified as the main source of cell-free DNA. Neutralizing cell-free DNA or inhibiting inflammasome activation reduced stroke recurrence, offering new perspectives for the prevention of early recurrent events …

Innate immune memory after stroke mediates secondary comorbidities.
July 2024 – ISD researchers hypothesized in a newly published study that the high rate of comorbidities that develop after a stroke could have a common immunological cause. A Myeloid innate immune memory was identified as causing remote organ dysfunction post-stroke. Single-cell sequencing revealed persistent pro-inflammatory changes in monocytes/macrophages up to 3 months after brain injury, especially in the heart, causing cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction. Neutralizing IL-1β or blocking monocyte trafficking prevented post-stroke cardiac dysfunction, suggesting immune-targeted therapies for secondary prevention …

Rational correction of disease-causing mutations in HTRA1
July 2024 – Rare mutations in HTRA1 cause cerebral vasculopathy and stroke. Using in vitro, in silico and in vivo analyses, the Dichgans lab in collaboration with colleagues from Duisburg established mechanistically distinct protein repair approaches to reverse the deleterious effects of pathogenic mutations interfering with the oligomeric assembly and protease function of HTRA1. Their findings exemplify the feasibility of rational strategies to correct protein conformations and open perspectives for precision medicine…

Rare and common HTRA1 variants affect stroke risk via two independent mechanisms
May 2024 – Combining genetic analyses in large international biobanks with experimental studies on human cells, ISD investigators found that rare HTRA1 variants affect vascular risk via a loss of enzymatic function of the HTRA1 protease, whereas a common causal variant independently affects vascular risk by influencing the circulating HTRA1 mRNA and protein levels. They further uncovered a complex relationship with other diseases including migraine and macular dystrophy.
Advanced Brain Science Without Coding Expertise
April 2024 – Researchers at ISD and Helmholtz Munich introduce DELiVR, offering a new AI-based approach to the complex task of brain cell mapping. The deep learning tool democratizes advanced neuroscience by eliminating the need for coding expertise. DELiVR empowers biologists to efficiently explore disease-related spatial cell dynamics, fostering the development of precision therapies for enhanced patient care. >>
Dysregulation of vesicular transport pathways during BEC aging
March 2024 – A proteomic profiling study on brain endothelial cells (BEC) by ISD investigators reveals a dysregulation of key regulators of endocytosis and receptor recycling (most prominently Arf6), macropinocytosis, and lysosomal degradation during aging. The study identified changes undetected in transcriptomic studies such as an accumulation of vesicle cargo and receptor ligands including Apoe. | Data are accessible via an interactive database https://becaging.de/
Role of CXCL10 as a causal mediator in Atherosclerosis
February 2024 – Integrating genetic information from >520,000 individuals with data from plasma proteomics, the team of Marios Georgakis identified a proteomic signature of IL-6 signaling activation and mediators of its effects on cardiovascular disease. Their analyses suggest, that the interferon-γ-inducible chemokine CXCL10 is a potentially causal mediator for atherosclerosis in different vascular beds (coronary, cerebral, and peripheral arteries) and could serve as a promising drug target for atheroprotection.
Changes in synapses related to protein 43 (GAP-43) speed up the spread of tau in AD
January 2024 – A combined neuroimaging and biofluid biomarker study investigated whether synaptic changes are associated with accelerated tau spreading in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Higher levels of the presynaptic protein GAP-43 speed up the spread of tau in AD. These findings by Nico Franzmeier (ISD) and others are relevant for developing treatments to slow down the progression of the disease. >>

Decoding strokes silent saboteurs
December 2023 – A study by Josh Shrouder within the Plesnila lab, together with collaborators reveals how dysfunction of capillary pericytes aggravates no-reflow after ischemic stroke. These longitudinal in vivo results challenge the notion that pericytes are terminally susceptible to ischemia, and demonstrate how acute interventions targeting pericyte constriction could be harnessed to accelerate the restoration of capillary blood flow and improve stroke outcome.
Influence by Imitation
November 2023 – A study by the Bernhagen Lab and collaborators shows that specific plant proteins resemble human signaling proteins of the immune system and can bind to their receptors. While representing basic cross-discipline research, the work might have translational implications, as the receptors are drivers of cardiovascular diseases and inflammation.
Identifying optimal treatment windows for patients at risk of Alzheimer's
November 2023 – A study by Anna Steward and Nicolai Franzmeier reveals that ApoE4 carriers experience faster and earlier disease progression due to amyloid's impact on tau. These results urge earlier intervention for ApoE4 carriers who show reduced efficacy in response to anti-amyloid drugs. This insight, crucial for 40-60% of sporadic AD cases, suggests a potential shift in therapy approaches, advocating for tailored clinical studies to validate this new paradigm.

Frontline results of the TREAT-SVDs trial
October 2023 – Main results from TREAT-SVDs, an EU funded multicenter, open-label, randomised, crossover trial were presented at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) in Munich and recently published in the Lancet Neurolgy. The results show that four weeks of treatment with amlodipine, losartan, or atenolol did not differ in their effects on cerebrovascular reactivity in people with sporadic small vessel disease but did result in differential treatment effects in patients with CADASIL.
Skull: A key new player in the neuro-immune axis
August 2023 – Neuroimmune interactions exhibit remarkable complexity, and exploring brain borders has gained significant attention in the quest for innovative approaches to diagnose, monitor, and treat brain pathologies. The recent discovery of connections between the skull and meninges has brought the skull into focus. A large collaborative research team led by the Erturk lab extensively examined the molecular and structural aspects of the skull in both mice and humans. Their findings demonstrated that skull inflammation can serve as an indicator of brain inflammation in patients suffering from diverse neurological disorders.

wildDISCO: A Revolutionary Whole Mouse Body Mapping Technique
July 2023 – Researchers at the Erturk lab have introduced wildDISCO, a groundbreaking method that utilizes standard antibodies to achieve deep penetration into the whole mouse body, generating high-resolution 3D atlases of neurons, immune cells, the vasculature, and lymphatic vessels. With unprecedented insights into anatomical and functional connections among multiple organs and systems, wildDISCO promises to revolutionize disease understanding, drug development, and medical education.
STRIVE-2 Standards released
May 2023 – Small vessel disease (SVD) accounts for ~25% of strokes, more than doubles the risk of future stroke, and contributes to up to 45% of dementia cases. In 2013, STandards for ReportIng Vascular Changes on nEuroimaging 1 (STRIVE-1) categorised features of SVD that are visible on structural MRI and defined standards on multiple levels up to reporting. In an international effort with other experts ISD investigators now updated guidance on imaging of vascular changes in studies of ageing and neurodegeneration to create STRIVE-2...
3D spatial-omics technology to tackle complicated diseases.
December 2022 – Identifying subtle tissue changes at disease initiation or characterizing the molecular perturbations that trigger disease progression remains difficult in animal models or post-mortem human organs. To address this challenge, ISD investigators developed DISCO-MS, a 3D spatial-omics technology that combines methods of tissue clearing with cutting edge AI, robotics and proteomics technologies. They applied DISCO-MS to an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model and to atherosclerotic plaques in the human heart to identify spatial-molecular maps...
CD8+ T cells induce IFN-responsive oligodendrocytes & microglia in white matter aging
October 2022 – Among the hallmarks of brain aging is a decline in white matter volume and function. Using scRNA-seq, the Gokce and Simons labs characterized age-related oligodendrocyte and microglial states. They identified a population of interferon-responsive oligodendrocytes (IRO) and microglia (IRM) that localize near CD8+ T cells in white matter. Lack of CD8+ T cells prevented age-related cell loss in white matter. Their findings unravel a so-far unknown role of the adaptive immune system during brain aging...
A shortcut to inflammasome activation
October 2022 – A rapid immune response to signals released from pathogens and injuries is critical for maintaining tissue integrity and restoring homeostasis. This response is largely mediated by the concerted action of pattern recognition receptors. Such cooperativity has been described for Toll like receptors (TLRs) and the NLRP3 inflammasome, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive. ISD investigators now demonstrate that IKKβ binds NLRP3 providing a shortcut to inflammasome activation for rapid immune responses...
Stroke genetics informs drug discovery and risk prediction across ancestries
September 2022 – A GWAS meta-analysis of >110,000 stroke patients and 1.5 Mio controls from five different ancestries identified multiple novel stroke risk loci. The study provides genetic evidence for putative drug effects with converging evidence for drugs targeting F11 and KLKB1 among others. Drugs targeting F11 and F11a are currently being examined in phase II trials for stroke prevention. A polygenic score predicted ischemic stroke across ancestries and in clinical-trial participants with cardiometabolic disease ...
Complicated Carotid Artery Plaques and Risk of Recurrent Ischemic Stroke or TIA
May 2022 – Complicated nonstenosing carotid artery plaques (CAPs) are an under-recognized cause of stroke. Applying high-resolution contrast-enhanced carotid MRI to patients with acute ischemic stroke, ISD investigators found complicated CAP ipsilateral to acute ischemic anterior circulation stroke to be associated with an increased risk of recurrent ischemic stroke or TIA. Carotid plaque imaging identifies high-risk patients who might be suited for inclusion into future secondary prevention trials...
Brain connectivity is associated with tau deposition in 4-repeat tauopathies
March 2022 – Tau pathology drives neuronal dysfunction in 4-repeat tauopathies. Here, ISD researchers combined tau-PET, resting-state fMRI and histopathology data, to show that brain connectivity is associated with tau deposition patterns in patients with 4-repeat tauopathies...
Role of HTRA1 in brain white matter hyperintensities
October 2021 – In a whole-exome sequencing study on >16.000 individuals, ISD investigators found rare variants in the protease domain of HTRA1 to associate with brain WMH burden. The frequency of such variants in the general population was 1:450 and their presence corresponded to a larger effect than meeting the criteria for conventional vascular risk factors. Variants in EGFL8, which falls into a common pathway with HTRA1, also associated with WMH burden…
Interneurons trigger cortical spreading depolarizations (CSDs)
September 2021 – CSDs are the electrophysiological correlate of migraine aura and involved in the propagation of brain damage after ischemic and traumatic brain injury. Using a novel migraine mouse model, the Plesnila Lab in collaboration with Tobias Freilinger, Holger Lerche (Tübingen, Germany), and Massimo Mantegazza (Nice, France) found that CSDs are triggered by inhibitory interneurons. This counterintuitive finding unravels the so far unknown cellular mechanism for the initiation of CSDs...
Role of complement component C4 in age-related white matter injury
July 2021 – Age-related loss of white matter integrity is a major determinant of cognitive decline and dementia. Analysing data from >30.000 UK Biobank participants, ISD investigators in collaboration with Matthew Traylor (London) found the complement component C4-BS variant to associate with age-related WM injury. These findings suggest a role of the complement systems and of gene-environment interactions in age-related loss of white matter microstructural integrity...
Common KLOTHO SNP protects against Tau pathology
June 2021 – ISD researchers found that a common variant in the anti-aging gene KLOTHO is associated with reduced fibrillar tau, a key pathology in Alzheimer’s disease...
Life’s simple 7 and incident dementia risk
March 2021 – Leveraging data from the UK Biobank (N=229,976 participants) ISD investigators examined whether cardiovascular health measured by the ‘Life’s simple 7’ score is associated with incident all-cause dementia. They found that higher blood pressure was associated with higher risk of dementia both in longitudinal and Mendelian Randomization analyses. These findings underscore the importance of blood pressure control in midlife to mitigate dementia risk...
Genetic downregulation of IL-6 signaling leads to a favourable cardiometabolic profile
March 2021 – Drugs targeting IL6 signaling have been approved for autoimmune diseases but the repurposing potential for other indications remains unknown. ISD researchers developed a genetic score predicting IL6 signaling activity over lifetime. In a phenome-wide association study they found genetically downregulated IL6 signaling to be associated with a favourable cardiometabolic profile including a lower risk of coronary artery disease and diabetes, and an increase in HDL cholesterol levels. Their results support repurposing of IL6R blockade as a strategy for lowering vascular risk...
AIM2-inflammasome signaling cascade causes post-stroke immunosuppression and secondary infections
March 2021 – Stroke patients are predisposed to life-threatening infections after the initial ischemic event. This phenomenon is caused by a severe state of post-injury immunosuppression, which is characterized by a loss of T cells. Stefan Roth (Liesz Lab) in collaboration with others demonstrates that monocytes sense injury-released cell-free DNA via the AIM2 inflammasome inducing extrinsic T cell death. Uncovering this mechanism could open up new therapeutical approaches...
White matter aging drives microglial diversity
February 2021 – Aging and vascular risk factors are associated with white matter (WM) lesions and loss, but the role of microglia in the aging WM has been elusive. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, ISD and DZNE investigators identified WM-associated microglia (WAMs), which form in a TREM2-dependent but APOE independent manner and are characterized by age-dependent activation of genes implicated in phagocytic activity and lipid metabolism. Thus, WAMs may represent a potentially protective response required to clear degenerated myelin accumulating during WM aging and disease...
Patient-centered prediction of tau spreading in Alzheimer’s
November 2020 – The spreading of tau pathology throughout the brain is the major driver of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. ISD researchers developed a new functional connectivity-based prediction model for the forecasting of future tau PET spreading patterns in Alzheimer’s disease patients. This patient-centered prediction model provides a precision-medicine tool for predicting disease progression and defining a patient-tailored outcome measure to boost power in clinical trials targeting tau pathology...
Designed chemokine receptor mimic blocks atherosclerosis by chemokine-specific targeting
November 2020 | Atherosclerosis is the main cause of stroke and myocardial infarction. While the inflammatory paradigm is established, the development of anti-cytokine/chemokine therapeutics for atherosclerosis has remained challenging. A team of investigators led by the Bernhagen (ISD) and Kapurniotu (TUM) labs designed peptide-based mimics of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 that block experimental atherosclerosis. The new compounds selectively target pro-atherogenic chemokine pathways, whereas homeostatic pathways are spared. The study is published in Nat Communications...
Complicated Carotid Artery Plaques as a Cause of Cryptogenic Stroke
November 2020 – In up to 30% of patients the aetiology of stroke remains unknown. Applying high-resolution contrast-enhanced carotid MRI to patients with acute ischemic stroke ISD investigators identified nonstenosing complicated carotid artery plaques (cCAP) as an underrecognized cause of stroke. The most frequent feature of ipsilateral cCAP was intraplaque haemorrhage (89%), which can be reliably detected by conventional MRI sequences. Whether integrating carotid MRI into the diagnostic workflow would add clinical decision-making remains to be explored...
Neuropilin-1 opens the door to SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity
November 2020 – An international research team, coordinated by Mikael Simons (DZNE) with participation of the Gokce Lab identified neuropilin-1 as a factor that facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells including of the central nervous system. The study is now published in “Science”.

Diffusion MRI alterations in the elderly are predominantly of vascular origin
August 2020 – Diffusion tensor imaging is widely used to study the brain microstructure, especially in memory clinic patients. The determinants of diffusion alterations are, however, largely unknown. A large-scale study led by ISD investigators addresses this important question by identifying cerebral small vessel disease as the main determinant of diffusion alterations...
Higher sTREM2 and microglia PET associated with lower amyloid accumulation.
August 2020 – Alterations in the brain’s immune response are associated with higher risk of Alzheimer’s dementia, but the effect of microglia activation on amyloid-plaque deposition is elusive. ISD and DZNE investigators found higher CSF sTREM2 and TSPO PET, i.e. biomarkers of microglia activation, to be associated with lower amyloid accumulation in both mouse models of amyloid deposition and elderly individuals, suggesting a protective effect of TREM2-related microglia activity against a key Alzheimer’s pathology...
Metabolic signature differentiates ischemic stroke from stroke mimics
August 2020 – Early discrimination of patients with ischemic stroke (IS) from stroke mimics (SM) is important to allocate treatments, but poses a diagnostic challenge. Applying untargeted metabolomics to serum samples from > 800 patients with stroke-like symptoms, ISD investigators identified a signature of circulating metabolites that differentiates IS from SM with higher accuracy than multimodal cranial computed tomography upon hospital admission...
Visualization of biocompatible nanoparticles
July 2020 – Biocompatible nanoparticles have huge therapeutic potential, but could so far not be visualized. In a collaboration with investigators from Strasbourg, Igor Khalin (Plesnila Lab) now demonstrates that specifically designed ultra-bright nanoparticles can be traced in vivo by 2-photon microscopy. This technological breakthrough greatly improves our understanding how to target therapeutic compounds to the CNS...
HDAC9 – from GWAS discovery to mechanisms and therapeutic targeting
June 2020 – Drug targets with support from human genetics have a higher probability of reaching phase III clinical trials and regulatory approval. Following their GWAS-based discovery of HDAC9 as a major risk locus for human atherosclerosis, ISD investigators identified a detailed mechanism linking HDAC9 to vascular inflammation. They further demonstrate that therapeutic inhibition of this HDAC9-dependent pathway confers plaque stability on top of atheroprotection …
Taming widespread collateral damage of CRISPR editing
May 2020 – CRISPR-Cas9 has revolutionized disease-research, as it greatly simplifies targeted genome editing. However, CRISPR systems are not entirely accurate and can introduce potentially harmful additional mutations, called on-target effects. In a collaborative study with the DichgansLab, the PaquetLab identified widespread prevalence of on-target effects in clinically relevant CRISPR-edited iPS cells and describes broadly applicable tools to detect these unintended alterations. The new method improves the reliability of CRISPR editing...
Machine learning analysis of whole mouse brain vasculature
March 2020 – The Ertürk lab in collaboration with others (ISD, Helmholtz Munich and TUM) developed an artifical intelligence aided tool to study the vasculature in complete transparent mouse brains. Using 3D microscopy, they visualized the underlying complex network of all brain vessels at the capillary level. Their new tool can generate reference maps of the adult mouse brain vasculature, which could be used to model synthetic cerebrovascular networks. On this basis, unknown vascular properties can be discovered and biological models can be confirmed...
Aβ deposition associated with white matter alterations in cognitive normal people
March 2020 – In an international collaboration, ISD researchers report increased amyloid PET uptake to be associated with higher age-related fiber tract alterations and white matter hyperintensities in cognitively asymptomatic people...
Transparent human organs – 3D maps at cellular level
February 2020 – The Ertürk lab (ISD and Helmholtz Munich) managed to make intact human organs transparent. Using microscopic imaging they visualized underlying complex structures of see-through organs at the cellular level. Resulting organ maps could serve as templates for 3D-bioprinting technologies. This eventually could contribute to the creation of on demand artificial organs for patients in need...
Higher sTREM2 and microglia PET associated with lower amyloid accumulation.
August 2020 | Alterations in the brain’s immune response are associated with higher risk of Alzheimer’s dementia, but the effect of microglia activation on amyloid-plaque deposition is elusive. ISD and DZNE investigators found higher CSF sTREM2 and TSPO PET, i.e. biomarkers of microglia activation, to be associated with lower amyloid accumulation in both mouse models of amyloid deposition and elderly individuals, suggesting a protective effect of TREM2-related microglia activity against a key Alzheimer’s pathology...
Ewers M, Biechele G, Suárez-Calvet M, Sacher C, Blume T, Morenas-Rodriguez E, Deming Y, Piccio L, Cruchaga C, Kleinberger G, Shaw L, Trojanowski JQ, Herms J, Dichgans M; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), Brendel M, Haass C, Franzmeier N. Higher CSF sTREM2 and microglia activation are associated with slower rates of beta-amyloid accumulation. EMBO Mol Med. 2020 Sep 7;12(9):e12308. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202012308. Epub 2020 Aug 10. PMID: 32790063; PMCID: PMC7507349.
Digital medicine model of cognitive worsening in Alzheimer’s disease
February 2020 – In a large collaborative study with the North American DIAN and ADNI studies, ISD researchers developed a fully automated and cross-validated machine-learning algorithm for the prediction of disease progression in Alzheimer’s disease. The biofluid and neuroimaging derived model allows to predict the rate of cognitive decline over a clinically relevant time window of 4 years….
Franzmeier N, Koutsouleris N, Benzinger T, Goate A, Karch CM, Fagan AM, McDade E, Duering M, Dichgans M, Levin J, Gordon BA, Lim YY, Masters CL, Rossor M, Fox NC, O'Connor A, Chhatwal J, Salloway S, Danek A, Hassenstab J, Schofield PR, Morris JC, Bateman RJ; Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI); Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (DIAN), Ewers M. Predicting sporadic Alzheimer's disease progression via inherited Alzheimer's disease-informed machine-learning. Alzheimers Dement. 2020 Mar;16(3):501-511. doi: 10.1002/alz.12032. Epub 2020 Feb 11. PMID: 32043733; PMCID: PMC7222030.
Role of HDL-C in cerebral Small Vessel Disease
January 2020 – Using Mendelian Randomization ISD investigators showed that genetic predisposition to higher HDL-C, specifically to cholesterol in medium-sized HDL, is associated with small vessel stroke and white matter injury. Their analyses indicate that HDL-C-raising strategies could be considered for the prevention of ischemic small vessel disease but the net benefit of such an approach needs to be tested in a randomized controlled trial...
Tau spreading associated with functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease
January 2020 – A multinational study led by the Ewers Lab and first author Nicolai Franzmeier shows that functional brain architecture predicts the spatial patterns of the gradual spreading of tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease, supporting in-vitro findings of trans-neuronal tau propagation...
Improved Genomic Risk Score (GRS) for Stroke
December 2019 – ISD researchers developed a metaGRS for ischaemic stroke (IS) that outperforms previous GRS and identifies a subset of individuals at monogenic levels of risk. Individuals in the top 0.25% of the metaGRS have a threefold increased risk of IS. The results suggest that, for individuals with a high metaGRS, achieving risk factor levels recommended by current guidelines may be insufficient to mitigate risk...
Deep Learning Reveals Therapeutic Antibody Targeting in the Entire Body
December 2019 – Combining clearing technology with deep learning algorithms ISD investigators developed an integrated pipeline for automated quantification of cancer metastases and therapeutic antibody targeting (DeepMACT) that enables analysing the size, shape, and spatial distribution of metastases, and the degree to which metastases are targeted by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies in entire mice...
Circulating MCP-1 levels associate with stroke risk
September 2019 – Expanding on their previous Mendelian Randomisation study (CIRCULATION 2019) ISD researchers now provide further evidence for a causal role of MCP-1 in stroke. In a meta-analysis of observational data from 17,180 stroke-free individuals they found higher circulating MCP-1 levels to be associated with long-term risk of incident ischemic stroke...
Protective effects of TREM2 in Alzheimer's Disease
August 2019 – The teams of M. Ewers and C. Haass found higher cerebrospinal fluid comcentrations of TREM2, a biomarker of microglia activation, to slow down cognitive decline in Alzheimer's Disaease...
Novel insights into small vessel disease progression
July 2019 – Using a prospective, high-frequency serial imaging study, a team of researchers at ISD and Radboudumc Nijmegen identified acute infarcts as the cause of incident lacunes and almost a third of incident microbleeds. In contrast, the progression of white matter hyperintensities was independent from acute infarcts. These new insights were enabled through a unique study design with monthly MRI exams...
BIN1 SNP associated with tau deposition in Alzheimer’s
April 2019 – A multinational study led by Michael Ewers and his team suggests that enhanced tau pathology may underlie the increased risk of Alzheimer’s conferred by the BIN1 single nucleotide polymorphism - the second most important genetic risk factor of AD...

BDNF-Val66Met SNP modulates hippocampus disconnection in Alzheimer’s
April 2019 – ISD researchers found a common variant in the BDNF gene to modulate the impact of amyloid pathology on hippocampal network connectivity and memory in Alzheimer’s disease...

Functional connectivity associated with tau pathology
February 2019 – A combined fMRI and tau PET study in Alzheimer’s disease by Michael Ewers and team shows that the spatial pattern of tau pathology is predicted by functional network connectivity, suggesting that cross-talk between brain regions is conducive to tau spreading...

Skull-meninges connections revealed by vDISCO
January 2019 – The Erturk group developed a nanobody-based immunolabeling method, vDISCO, that enables imaging subcellular details in transparent mice. They uncovered neuronal projections and skull–meninges connections in whole adult mice that are likely to have relevance in both health and disease...

Novel risk loci for stroke
November 2018 – A genome-wide meta-analysis involving almost 900.00 subjects from the MEGASTROKE consortium and UK Biobank identified new risk loci for stroke among them endothelial nitric oxide synthase (NOS3). The study further suggests that genetic variation in the NOS - nitric oxide (NO) pathway in part affects stroke risk via variation in blood pressure...

Role of Monocyte Chemo-attractant Protein-1 in stroke
Using a Mendelian Randomization approach and data from >800.000 individuals ISD investigators showed that genetic predisposition to higher levels of the inflammatory cytokine MCP-1 is associated with a higher risk of stroke, in particular large artery stroke and cardioembolic stroke. These findings inform the planning of future clinical trials...

White matter alterations precede symptom onset in Alzheimer’s dementia
Ewers and his team found the evolution of white matter alterations to start in callosal fibers already 10 years before estimated symptoms onset in familial Alzheimer’s disease...
Franzmeier N, Koutsouleris N, Benzinger T, Goate A, Karch CM, Fagan AM, McDade E, Duering M, Dichgans M, Levin J, Gordon BA, Lim YY, Masters CL, Rossor M, Fox NC, O'Connor A, Chhatwal J, Salloway S, Danek A, Hassenstab J, Schofield PR, Morris JC, Bateman RJ; Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI); Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (DIAN), Ewers M. Predicting sporadic Alzheimer's disease progression via inherited Alzheimer's disease-informed machine-learning. Alzheimers Dement. 2020 Feb 11. [Epub ahead of print]












































